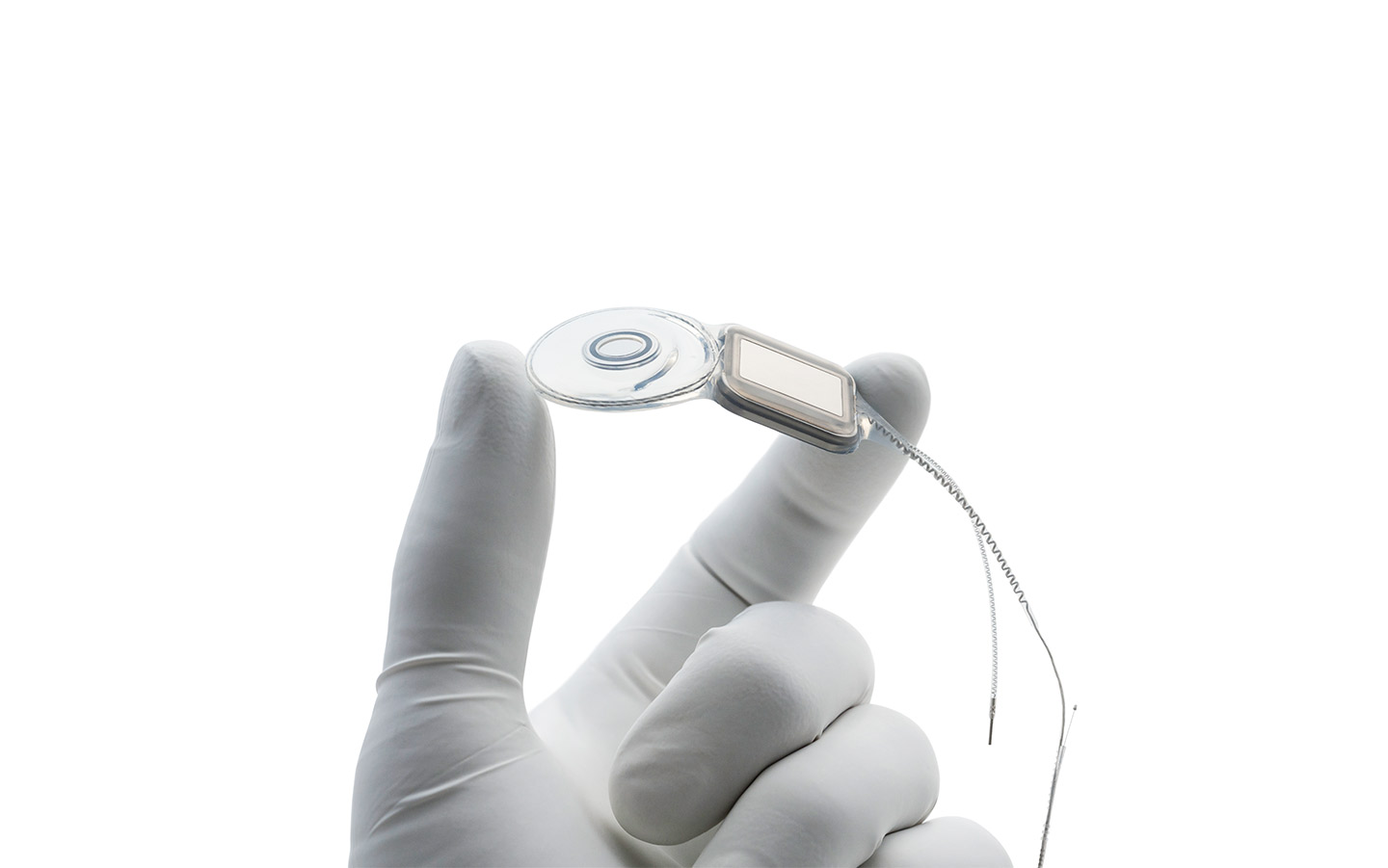
Nucleus® implants
Cochlear has a range of implants and electrodes for your type of hearing loss and cochlea anatomy. Discover what sets Nucleus® implants apart.

What you'll find on this page
- How we design Cochlear™ Nucleus® implants.
- The Cochlear Nucleus implant portfolio.
- The link between electrode design and hearing performance.
Cochlear's implant design philosophy
-
Designed to last.
-
Produce superior hearing performance.
-
Suit the unique anatomy of your ear.
-
Support advances in sound processor technology.
World's thinnest cochlear implants
The Nucleus® Profile™ and Profile Plus Series implants are the thinnest in the world.*
They are designed with a flexible coil to better fit the natural shape of your head.
Both Profile Plus and Profile Series Implants also have a high impact resistance — up to 2.5 joules — which meets the European standards for impact testing.
Industry-leading design for hearing performance
The anatomy of the cochlea varies from person to person. That's why we offer a range of electrode shapes and lengths. Your surgeon will decide which one is best for you.
Unique features of Cochlear's electrodes and implants include:
-
22 active contacts for maximum frequency coverage.
-
The world's thinnest full-length electrode.
-
Electrodes which sit closest to the hearing nerve for your best hearing performance.1,2
-
Best long-term implant reliability record in the industry.*3

Disclaimer
Please seek advice from your health professional about treatments for hearing loss. Outcomes may vary, and your health professional will advise you about the factors which could affect your outcome. Always read the instructions for use. Not all products are available in all countries. Please contact your local Cochlear representative for product information.
For a full list of Cochlear’s trademarks, please visit our Terms of Use page.
References
*Unless magnet removal is necessary to reduce image artefact. If you need an MRI scan of your head, your cochlear implant magnet may need to be removed because it will distort the scan image at any MRI strength. If your magnet does need to be removed, you can feel confident that the design of the Profile Plus Series Implant makes this as swift and straightforward as possible.
- The following implants are designed to be compatible for MRI at 1.5 T and at 3.0 T with the magnet in place: Nucleus Profile Plus: CI612, CI622, CI632.
- Compared to all currently available receiver stimulators available from Cochlear and other cochlear implant manufacturers. Based on published device specification information.
- Ramos de Miguel A, Argudo AA, Borkoski Barreiro SA, Falcon Gonzalez JC, Ramos Macias A. Imaging evaluation of electrode placement and effect on electrode discrimination on different cochlear implant electrode arrays. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Jun;275(6):1385-1394.
- Hughes ML, Abbas PJ. Electrophysiologic channel interaction, electrode pitch ranking, and behavioral threshold in straight versus perimodiolar cochlear implant electrode arrays. J Acoust Soc Am 2006; 119: 1538-47.
- Xi X, Ji F, Han D, Hong M, Chen A. Electrode interaction in cochlear implant recipients: comparison of straight and contour electrode arrays. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 2009; 71: 228-37.
- Basta D, Todt I, Ernst A. Audiological outcome of the pull-back technique in cochlear implantees. Laryngoscope 2010; 120: 1391-6.
- Saunders E, Cohen L, Aschendorff A, Shapiro W, Knight M, Stecker M, et al. Threshold, comfortable level and impedance changes as a function of electrode-modiolar distance. Ear Hear 2002; 23(1 Suppl): 28S-40S.
- Parkinson AJ, Arcaroli J, Staller SJ, Arndt PL, Cosgriff A, Ebinger K. The nucleus 24 contour cochlear implant system: adult clinical trial results. Ear Hear 2002; 23(1 Suppl): 41S-8S.
- Shaul C, Dragovic AS, Stringer AK, O’Leary SJ, Briggs RJ. Scalar localisation of peri-modiolar electrodes and speech perception outcomes. J Laryngol Otol. 2018;132:1000–6.
- Cuda D, Murri A. Cochlear implantation with the nucleus slim modiolar electrode (CI532): a preliminary experience. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;274:4141–8
- Hey, M, Hoppe, U, Stöver T, Baumann U, Mewes A, Liebscher T, Schüssler M, Aschendorrf A, Wesarg T, Büchner A, Neben N. Retrospective Hearing Performance Outcome in a Larger Cohort of CI532 Recipients; , Poster presented at 10th International Symposium on Objectives Measures in Auditory Implants (OMAI), October 2018.
- Friedmann DR, Kamen E, Choudhury B, Roland JT, Jr; Surgical Experience and Early Outcomes With a Slim Perimodiolar Electrode Otol Neurotol. 2019 Mar;40(3):e304-e10 NYU Cochlear Implant Center, New York (USA)
- Holder JT, Yawn RJ, Nassiri AM, Dwyer RT, Rivas A, Labadie RF, Gifford RH. Matched Cohort Comparison Indicates Superiority of Precurved Electrode Arrays. Otol Neurotol 2019 Oct;40(9):1160-1166.
- International Standard ISO 5841-2. Implants for Surgery – Cardiac Pacemakers – Part 2: Reporting of Clinical Performance of Populations of Pulse Generators or Leads. Geneva (Switzerland): International Organization for Standardization. 2000.
- International standard ISO 5841-2. Implants for Surgery – Cardiac Pacemakers – Part 2: Reporting of Clinical Performance of Populations of Pulse Generators or Leads. Geneva (Switzerland): International Organization for Standardisation.2014.
- European Consensus Statement on Cochlear Implant Failures and Explanations. Otol Neurotol. 2005 Nov;26(6):1097-9.
- Battmer RD, Backous DD, Balkany TJ, Briggs RJ, Gantz BJ, van Hassell A, et al. International Classification of Reliability for Implanted Cochlear Implant Receiver Stimulators. Otol Neurotol.2010 Oct;31(8):1190-3.
- Cochlear Limited. D1932780 Cochlear Nucleus Reliability Report Volume 20 December 2021, March 2022.
Hearing Implant Reliability Reporting | MED-EL [Internet]. Medel.com. 2020 [cited 25 February 2020]. Available from: http://www.medel.com/hearing-solutions/cochlear-implants/reliability - 2019 Global Implant Reliability Report. 027-N025-02 RevC. Advanced Bionics AG and affiliates.; 2010 [cited 23 March 2020]. Available from: https://advancedbionics.com/content/dam/advancedbionics/Documents/Global/en_ce/Professional/Technical-Reports/Reliability/027-N025-02-RevCReliabilityReport2019CochlearImplant_RS.pdf.
- MED-EL does not report number of registered cochlear implants.